Australian researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery in the treatment of lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease. This discovery offers hope for effective long-term treatment, potentially revolutionizing the management of lupus and other autoimmune conditions.
Published Study
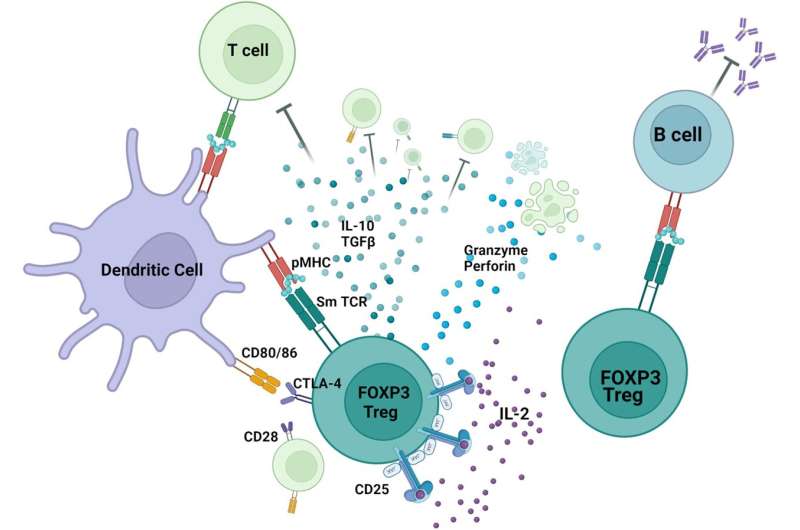
The study, led by Monash University and published in Nature Communications, reveals a novel approach to reprogramming defective cells in lupus patients using protective molecules from healthy individuals.
Restoring Immune System Balance
The treatment involves restoring the protective aspect of the immune system, which prevents autoimmunity – the condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells. By reprogramming the defective cells, the treatment aims to restore the function of regulatory T cells (T-regs), crucial in preventing autoimmune diseases like lupus.
Potential for Other Autoimmune Diseases
Researchers envision extending this method to treat other autoimmune diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. This could mark a significant advancement in the treatment of various autoimmune conditions.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- What is the focus of the research conducted by Australian scientists at Monash University?
- A) Developing vaccines for infectious diseases
- B) Identifying protective molecules for lupus treatment
- C) Studying the effects of climate change on autoimmune diseases
- D) Investigating surgical procedures for autoimmune disorders
- Answer: B) Identifying protective molecules for lupus treatment
- What is the role of regulatory T cells (T-regs) in the immune system?
- A) Promoting inflammation
- B) Attacking healthy cells
- C) Preventing autoimmune reactions
- D) Stimulating allergic responses
- Answer: C) Preventing autoimmune reactions
- What distinguishes lupus patients from healthy individuals concerning regulatory T cells?
- A) Lupus patients have fewer regulatory T cells
- B) Lupus patients have more regulatory T cells
- C) Lupus patients have identical regulatory T cells
- D) Lupus patients’ regulatory T cells are unaffected
- Answer: A) Lupus patients have fewer regulatory T cells
- According to the study, which immune component is lacking in individuals with lupus and other autoimmune conditions?
- A) B cells
- B) Natural killer cells
- C) Regulatory T cells
- D) Helper T cells
- Answer: C) Regulatory T cells
- What is the significance of the treatment approach developed by the researchers?
- A) It eliminates the need for any immunosuppressant drugs.
- B) It involves invasive surgical procedures.
- C) It primarily targets symptoms rather than the underlying cause.
- D) It relies solely on generic medications.
- Answer: A) It eliminates the need for any immunosuppressant drugs.