The Kerala government confirmed two cases of the ‘highly-contagious’ Norovirus in two children. According to the state health department, precautionary measures have been taken as the virus is believed to spread through contaminated water and food.

What is Norovirus?
Norovirus is a very contagious virus that causes vomiting and diarrhea. Anyone can get infected and sick with norovirus. Norovirus results in about 685 million cases of disease and 200,000 deaths globally a year.
Norovirus infection can cause severe vomiting and diarrhea that start suddenly. Noroviruses are highly contagious. They commonly spread through food or water that is contaminated during preparation or through contaminated surfaces. Noroviruses can also spread through close contact with a person who has norovirus infection.
Diarrhea, stomach pain and vomiting typically begin 12 to 48 hours after exposure. Norovirus infection symptoms usually last 1 to 3 days. Most people recover completely without treatment. However, for some people — especially young children, older adults and people with other medical conditions — vomiting and diarrhea can be severely dehydrating and require medical attention.
Symptoms of Norovirus
Signs and symptoms usually begin 12 to 48 hours after your first exposure to a norovirus and last 1 to 3 days. Signs and symptoms of norovirus infection may start suddenly and include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stomach pain or cramps
- Watery or loose diarrhea
- Feeling ill
- Low-grade fever
- Muscle pain
Causes of Norovirus
You can get norovirus infection by:
- Eating contaminated food
- Drinking contaminated water
- Touching your hand to your mouth after your hand has been in contact with a contaminated surface or object
- Being in close contact with a person who has norovirus infection
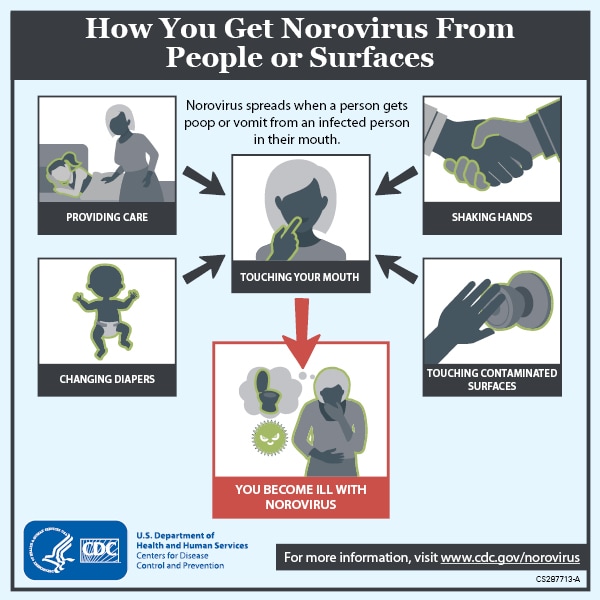
Prevention of Norovirus
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid contaminated food and water.
- Wash fruits and vegetables before eating.
- Cook seafood thoroughly.
- Use caution when traveling.
