Posted inTechnology News
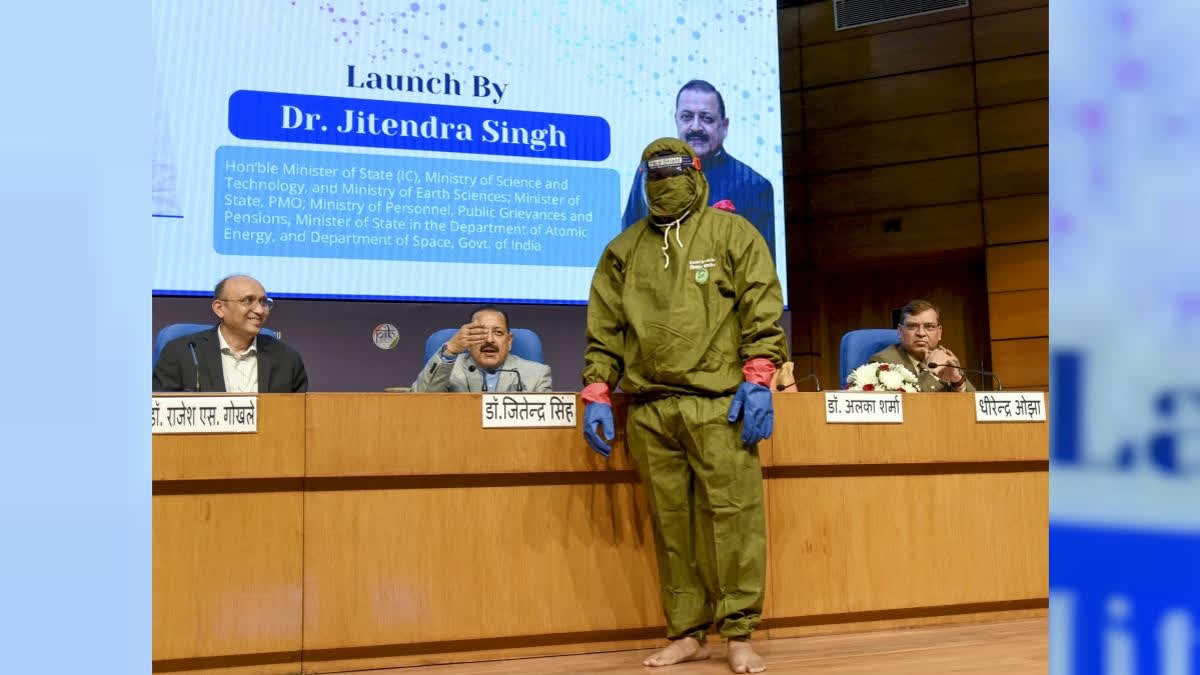
‘Kisan Kavach’: Innovative Protective Gear to Safeguard Farmers from Pesticide Exposure
In a significant development aimed at improving the health and safety of farmers, scientists have introduced the 'Kisan Kavach,' a protective gear designed to shield farmers from harmful pesticide exposure. This lightweight and durable gear acts as a barrier, preventing direct contact with dangerous chemicals commonly used in agricultural sprays. By reducing the risk of health issues such as skin irritation and long-term conditions, the 'Kisan Kavach' ensures that farmers can work safely and comfortably in the fields. This innovation not only promotes better health outcomes for farmers but also aligns with efforts to make farming practices more sustainable and safer.

























)





















)






)























)


)
)




)


